| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 미래에셋해외교환
- gradient descent
- Python
- set method
- electrochemical models
- 청춘 화이팅
- 유럽 교환학생
- fatigue fracture
- 특별 메소드
- li-ion
- m1 anaconda 설치
- special method
- 미래에셋 장학생
- 유럽
- 딥러닝
- Linear Regression
- 교환학생
- fluent python
- 이차전지
- 양극재
- 2022년
- 나의23살
- Machine learning
- anaconda 가상환경
- cost function
- Deeplearning
- Andrew ng
- 선형회귀
- 오스트리아
- set add
- Today
- Total
Done is Better Than Perfect
[ Paper Review ] Parameters for degradation diagnosis 본문
Effective and practical parameters of electrochemical Li-ion battery models for degradation diagnosis
- Journal : Energy Storage’ 21 (IF 8.9)
- 32 citations
[Summary]
- params 중에는 fixed params, dynamic params가 있음
- 15개의 dynamic params는 aging에 따라 변함
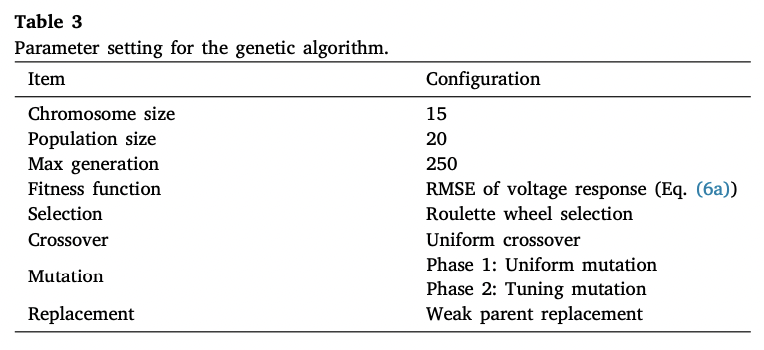
- 15개의 params에 대해 GA 알고리즘으로 파라미터 최적화
- 15개의 params 중에 battery degradation diagnosis하는 파라미터 선택
- 3가지 수렴 조건 , CI (Confidence Interval) 사용
- 결과 : degradation diagnosis 파라미터
- cathode particle surface area
- porosity
- stoichiometry limits
+) 일반화를 위해 3개의 profile에서 실행
1. Problem Statement
- SOH(State of Health) is not enough for diagnosis of the battery’s internal state
- SOH is defined using capacity, internal resistance (the ratio of the present capacity to initial one / the present equivalent series resistance)
- Capacity, internal resistance are insufficient to describe the current state of battery
- This paper proposes a practical method for identifying and selecting effective P2D model parameters that change significantly as a battery ages
⇒ Main theme : Identify more effective indicator(params) for accurate degradation diagnosis
2. Contribution
- P2D model parameters of a Li-ion battery were identified and their confidence intervals were analyzed
- Various operation profiles were used to avoid overfitting problems during parameter identification (generalization)
- Define aging parameters for battery degradation diagnosis
3. Methodology
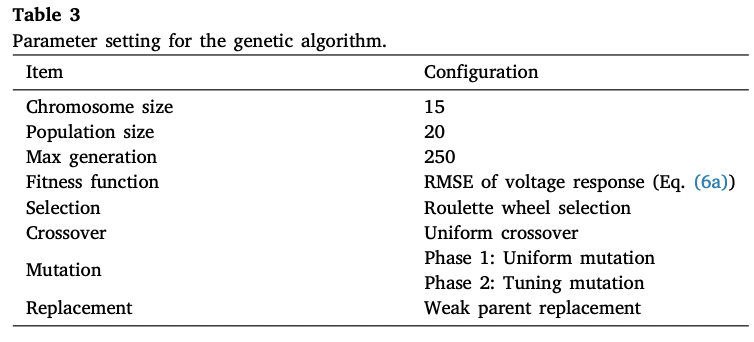
- Aim1 : Parameter Optimization using Genetic Algorithm
- Aim2 : Select ‘degradation diagnosis params’ among aging params
1️⃣ Select 15 dynamic parameters (vary with battery aging) in P2D model

2️⃣ Parameter Optimization using Genetic Algorithm
- Initial population generated randomly according to the designated search range
- Select parent chromosome by the roulette wheel algorithm
- Apply genetic algorithm - uniform mutation, tuning mutation
- Calculate fitness function for parameter combination (parent chromosomes)
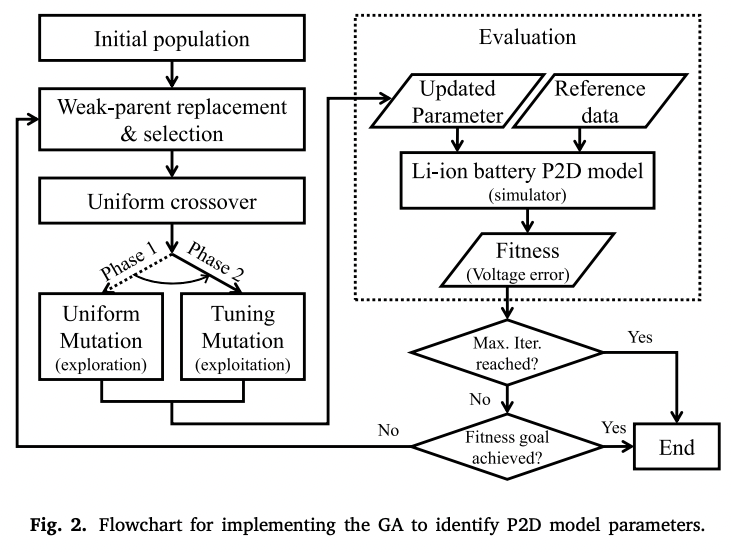

3️⃣ Select ‘degradation diagnosis params’ among aging params (using convergence criteria & CI )
[ criteria ]
- The parameters should converge to similar values for any initial condition and sample trajectory in the P2D model
- The parameters at BOL and EOL should converge to distinguishable values
- Parameter variation from BOL to EOL should be physically appropriate
4️⃣ Result : params for LIB degradation diagnosis

4. Experiment Result Analysis
4.1 Experimental Setup
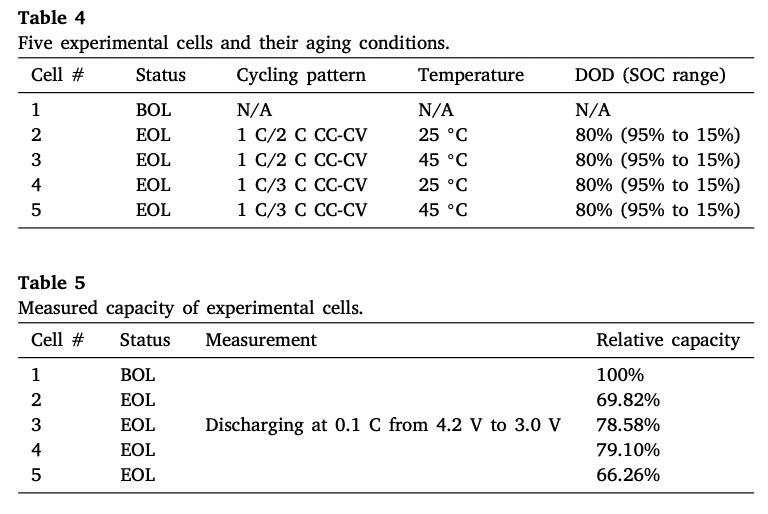
- Experiment with 5 cells :
- cell #1 - BOL(beginning-of-life battery)
- rest - EOL (end-of-life battery)
- Profile setting : CC-CV / HPPC / Driving cycle
- purpose
- Avoid overfitting issues during parameter identification
- Identify parameters that can reflect the characteristics of the battery under various operating conditions
- purpose
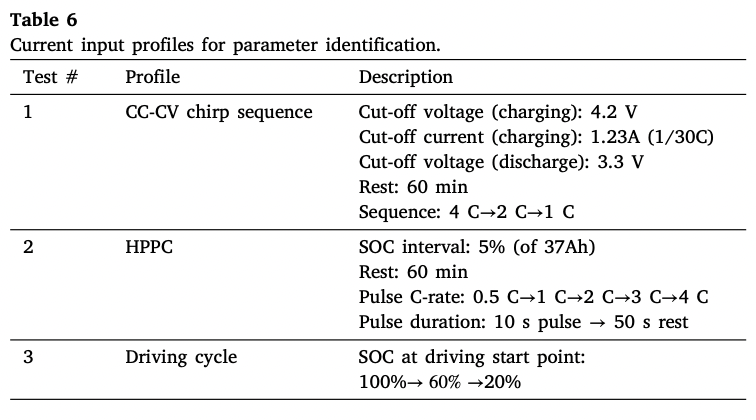
- CC-CV : observe battery response at various charge/discharge rates
- HPPC : observe pulse response at various SOC and current levels
- Driving cycle : simulate real electric vehicle usage patterns
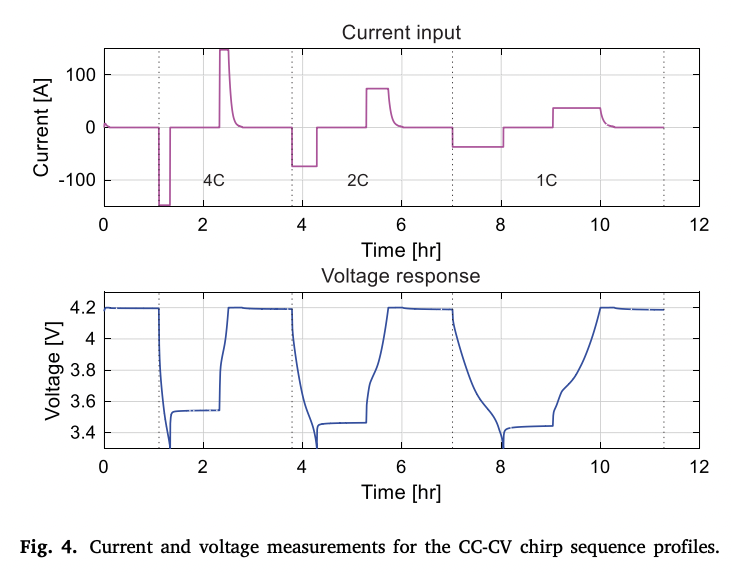
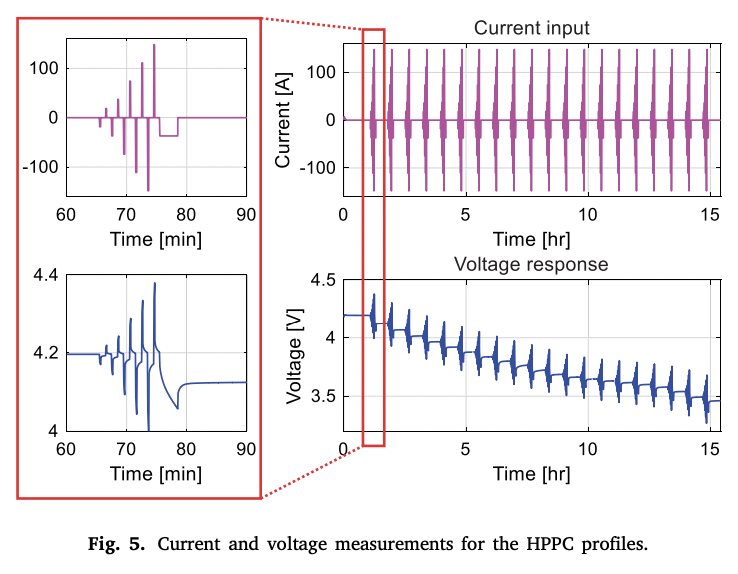
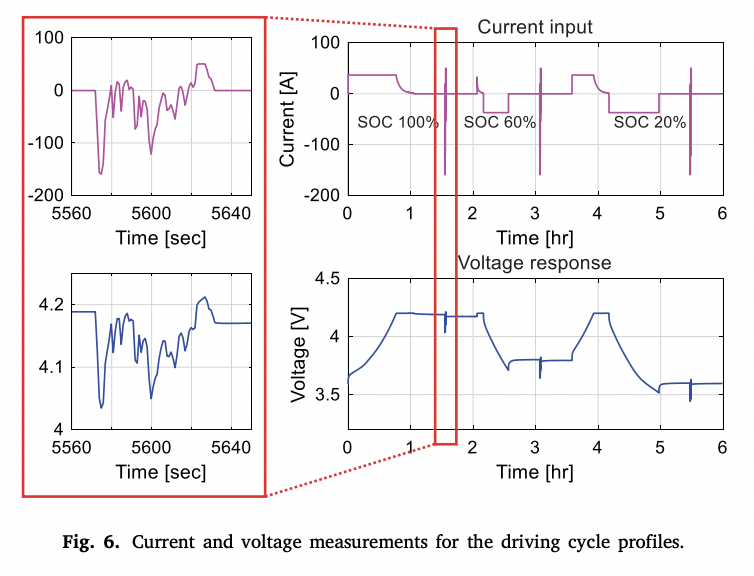
4.2 Result Analysis
4.2.1 Parameter identification results
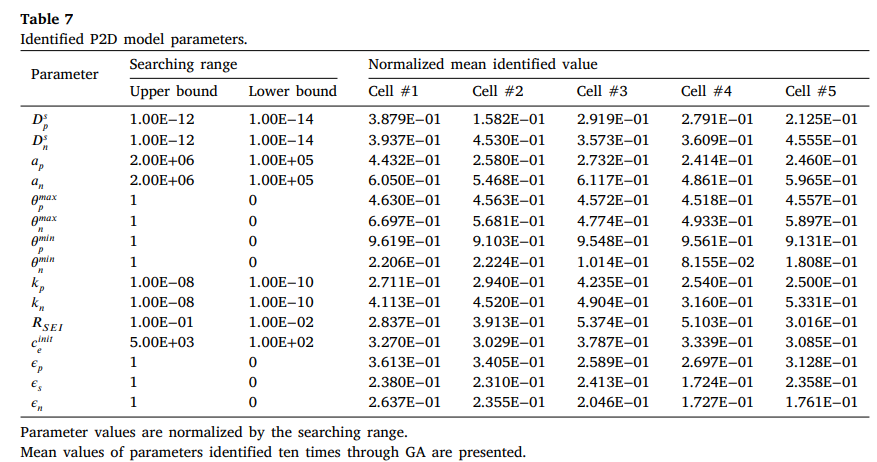
1-1. obtained optimization paramter value using GA

1-2. voltage error
To verify the reliability of the optimized parameter values

- Identified params show small voltage errors compared to existing result → Identified params using GA is effective
- CC-CV voltage error bigger than others
- OCV fitting error
- CC-CV profile has only one continuous dataset
4.2.2 Aging parameter selection
Select effective and practical aging parameters for battery degradation diagnosis
[ Criteria ]
- The parameters should converge to similar values for any initial condition and sample trajectory in the P2D model
- The parameters at BOL and EOL should converge to distinguishable values
- Parameter variation from BOL to EOL should be physically appropriate
[ Confidence Interval (using Table.8, Fig.10) ]


- cathode particle suface area (a_p)
- BOL과 EOL에서 구별 가능한 값으로 converge
- EOL에서 값이 감소하는 경향을 보임 → 반복된 충방전으로 인한 particle isolation, active dissolution ans cracking of the active marterial, SEI layer formatio 등으로 설명 가능
- stoichiometry limits (θmaxp, θmaxn, θminp, θminn)
- BOL과 EOL에서 구별 가능한 값으로 converge
- Theoretically, battery aging에 따른 reduction of active material → 각 전극에서 less lithiated state
- porosity (εp, εs, εn)
- 상대적으로 큰 CI을 가지지만, EOL에서 값이 감소하는 경향을 보임
- corresponding params converge to similar values for any initial condition
- Theoretically, porosity may play a role as diagnosing the degradation status of battery
5. Conclusion
Define aging parameters for battery degradation diagnosis :

[ Limitations and weakness ]
- This study deals with BOL and EOL cells only
- The middle of life (MOL) cells were not available
- Difficult to elaborately predict the intermediate stage of degradation
- Large confidence intervals for anode stoichiometry
- OCP of the anode has a potential plateau(평탄 구간) over a wide range
→ response of potential to lithium concentration change is very weak - difficult to make the stoichiometry limits converge using the proposed scheme that considers the output voltage error to be a fitness functionLarge confidence intervals for anode stoichiometry
- OCP of the anode has a potential plateau(평탄 구간) over a wide range

- Too small number of samples
- Identification performed 10 times for each cell using GA
- CI is calculated using the t-distribution ( less than 30 )
- The more parameter samples identified, the narrower the confidence interval
- Validation limits of identified parameters
- validate thorugh comparison with measured real voltage outputs
- For more accurate validation, true parameters should be directly compared (True parameters are measured with non-destructive and non-invasive test methods (EQCM-D) or X-ray tomography)
Background Knowledge
- P2D model

The governing equations of the P2D model (5 equations) :


- Genetic Algorithm
- Roulette wheel 방식으로 부모 염색체 선정 → fitness가 높을수록 부모로 선택될 확률이 높아지는 방식
- fitness가 높은 염색체가 더 높은 확률로 선택되도록 선택 영역 조정 가능
❓질의 응답
Q. 3개의 profile으로 실험한 이유
→ To identify selected aging parameters distinctly correlated with the battery degradation states
Q. BOL , EOL 구분해서 실험한 이유
→ 배터리의 Beginning-of-Life (BOL) 및 End-of-Life (EOL) 시에 뚜렷한 상이한 값으로 수렴하는 특정 파라미터가 aging parameter로 선택
→ 배터리 열화를 진단하기 때문에, 다양한 aging의 배터리 상태에서 실험하는 것이 적절함





